Zeiss Atlas 995 Manual
- Zeiss Atlas 9000 is Simply Accurate with Greater Productivity through Connectivity. The Zeiss Atlas 9000 Corneal Topographer is one of the best diagnostics instruments that enable eye care professionals to correctly and precisely measure the curvature of the cornea and to facilitate the production of very clear topographical images.
- CARL ZEISS Humphrey Atlas 995 Corneal Topographer with Windows 98 OS, Printer, Keyboard and Manual. Refurbished Zeiss Atlas 995 Corneal Topographer Features ATLAS's exceptionally small footprint integrates computer and monitor, and minimizes required table space.
- Cadex Cpb23 35 Manual Camera Zeiss Atlas 995 Manual Lymphatic Drainage Reno Police Department Ride Along Program Liability Grundig Sonoclock 410 Manual Dexterity Blast Effects On Buildings Pdf Download Evangelion Episode 24 Download Raw Theme Australia.fbl Map 2012 Dvdfab 8.
- Zeiss Atlas 995 Manual High School Serial Key For Total Network Inventory 1.6.8 Eminem Slim Shady Lp 320 Download Zip Sharebeast Hatsune Miku Project Diva 2nd Song List Download Mitsubishi Triton 2015 Workshop Manual Guitar Rig 5 Pro Mac Cracked Realbasic.
Description
Zeiss Atlas 9000 is Simply Accurate with Greater Productivity through Connectivity. The Zeiss Atlas 9000 Corneal Topographer is one of the best diagnostics instruments that enable eye care professionals to correctly and precisely measure the curvature of the cornea and to facilitate the production of very clear topographical images. The design of the equipment is such that it has the ability.
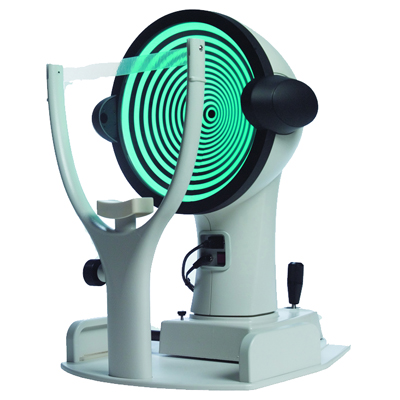
The Zeiss Atlas 995 Corneal Topographer is one of the most advanced systems available that offers ultra-low illumination and increased peripheral coverage and is also ideal for high volume corneal and contact lens specialists who require comprehensive and detailed peripheral corneal and pupil assessments. The greatest advantage of corneal topography is its ability to detect irregular conditions of your cornea invisible to most conventional testing. Since the Zeiss Atlas 995 can save your exam information, a practice can monitor any changes to the patient’s cornea and their corneal stability over time.
The Zeiss Atlas 995 corneal topographer consists of a computer linked to a lighted bowl that contains a pattern of rings. During a diagnostic test, a patient sits in front of the bowl with their head pressed against a bar while a series of data points are generated. The Zeiss Atlas 995’s computer software digitizes these data points to produce a printout of the corneal shape, using different colors to identify different elevations, much like a topographic map of the earth displays changes in the land surface. This is a painless and brief non-contact test.
Zeiss Humphrey Atlas 995 Features:
- Atlas 995 advanced Arc-Step Algorithm gives true elevation data
- 22-Ring Placido Cone presents a larger limbus-to-limbus field of view and it’s ideal spacing avoids ring crossover
- Zeiss Atlas 995 aspheric surface reconstruction
- Atlas 995 22-ring Conical Placido – Larger limbus-to-limbus field of view
- Zeiss Atlas 995 patented Cone-of-Focus superior electronic alignment for greater repeatability and accuracy
- Atlas 995atented chin rest design which eliminates nose shadow artifacts
- Zeiss Atlas 995 automatic Pupil Measurement
- Atlas 995 infrared chin rest sensors
- Zeiss Atlas 995 instant eye identification without operator input
This Zeiss Atlas 995 Topographer comes equipped with:
- 6 Month warranty
- Keyboard
- Digital Manual
- Dust Cover
Determining Corneal Power after Radial Keratotomy.
Unlike ablative forms of myopic keratorefractive surgery (LASIK and PRK) in whichthe ratio between the posterior : anterior corneal radii is decreased, for eyes thathave previously undergone radial keratotomy, the ratio between the posterior : anteriorcorneal radii is increased. This allows for a direct estimation of the central cornealpower using elevation data of the central 4.0 mm, if carried out in a certain way.
Image above: Zeiss Atlas Topographer, Annular Ring Power from the Numerical View feature. Use the average of the 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm and 4 mm annular power values. |
For eyes with prior radial keratotomy, averaging the 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm and 4 mm annular power rings of the Numerical View of the 995, 994, and 993 Zeiss Atlas topographer (right) will typically give a useful estimate of central corneal power.
For the Zeiss Atlas 9000 topographer, you would take average of the 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm and 4 mm ring (not zone) values. If the Zeiss Atlas topographer is not available, then the adjusted effective refractive power (EffRPadj) from the Holladay Diagnostic Summary of the EyeSys Corneal Analysis System can be used.
Above image: Axial curvature map from the Zeiss Atlas 9000 topographer displaying the ring values. For prior RK, the 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm and 4 mm ring values are used to estimate the central corneal power.
The key concept here is that we are looking to discover the corneal power at its center. Instruments such as manual keratometers, autokeratometers, or simulated keratometry using a standard topographer will typically over-estimate the central corneal power, resulting in a post-operative hyperopic surprise.
Of course, correctly estimating the central corneal power following RK is only half of the exercise. The calculated IOL power must also be adjusted to prevent the artifact of a very flat central corneal power from having the formula underestimate IOL power. Follow this link: 2-variable IOL Power Formulas for a summary of why this is so and how this is carried out.
Transient hyperopia following cataract surgery and prior radial keratotomy

Zeiss Atlas 995 Manual Review
Patients with previous 8-incision radial keratotomy will commonly show variable amounts of transient hyperopia in the immediate post-operative period following cataract surgery. This is felt to be due to stromal edema around the radial incisions, producing a temporary enhancement of central corneal flattening. While this central corneal flattening is usually transient, it can be as much as +4.00 D, and is further accentuated by greater than eight incisions, an optical zone of less than 2.0 mm, or incisions that extend all the way to the limbus.
If a patient exhibits any of the above, significant unanticipated hyperopia may be seen in the immediate post-operative period, which should gradually resolve after eight to twelve weeks. Sometimes, due to a lack of corneal stability, the post-operative refraction can continue to slowly shift myopic over a several month period. We have seen several patients with myopic shifts as large a -5.00 D over a 12-week period.
Zeiss Atlas 995 Manual 2
If the final post-operative refractive objective remains elusive, plans for an IOL exchange, or a piggyback IOL, should not be made until at least two months have passed and two consecutive refractions, two weeks apart (at the same time of the day), are stable (the 'rule of twos.').
Also, if more than six months passes before cataract surgery is required for the fellow eye, the corneal measurements should be repeated due to the fact that additional corneal flattening frequently occurs over time following radial keratotomy. For this reason, IOL power calculations are usually targeted for between -0.75 D and -1.00 D and are designed to make the operative eye more myopic than usual, so that five to ten years from surgery, the post-cataract surgery refractive error does not drift into hyperopia. This also helps to avoid hyperopic refractive results, which are quite common, in spite of every precaution being taken.
Of all the various forms of keratorefractive surgery, we have had the best overall accuracy following radial keratotomy using the above technique.